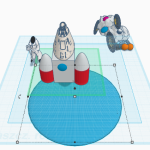
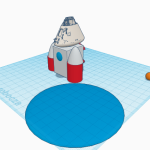
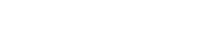Base Espacial con Tinkercad by Equipo 3A7
IES Cristobal de Monroy Alcalá de Guadaira-Sevilla Spain 15 years old 4 / Spanish Moon
External link for Tinkercad 3D design
Project description
SECCION 1: MI CAMPAMENTO ESPACIAL
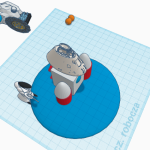
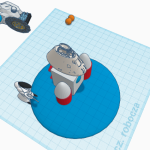
1- En el proyecto hemos distintas fases, al principio hicimos una iniciación en Tinkercad para aprender a manejarnos con la aplicación y a partir de hay hemos creado distintos objetos ayudándonos con videos de YouTube que nos decían las medidas,los objetos…Y entre ellos hemos hecho un rober lunar, un invernadero lunar, un astronauta, un cohete y módulos habitables para después unirlo todo y crear un campamento lunar de astronautas para que puedan seguir viviendo, investigando la luna…
También hemos estado haciendo lecturas a través de páginas webs con contenido sobre la luna, viajes hacia ella, como sobrevivir en el espacio, como construir… y después teníamos que responder unas preguntas sobre ese tema y las respuestas las teníamos que sacar de la página web.
SECCION 2: CONSTRUIR UN CAMPAMENTO ESPACIAL
3- Seguramente el campamento espacial sea construido en ubicado en el cráter Shackleton en el polo sur de nuestro satélite, porque está casi constantemente iluminado y hay hielo de agua en el cráter. La base está en la superficie, lo que simplificará enormemente la construcción. Se cubrirá con una capa de tierra.
4-Los habitantes de la Luna tendrían que construir edificios con paredes lo suficientemente gruesas para bloquear la entrada de radiación y usar trajes espaciales engorrosos cada vez que salen al exterior.
Estas consideraciones significan que, cuando expandamos las primeras bases y comencemos a construir estructuras en la Luna, el concreto lunar, que es una mezcla
de azufre y agregado (granos o roca triturada; el concreto normal es agregado, cemento y agua) puede ser una buen opción.
5- Porque tienen todas las necesidades que le satisfacen poder vivir durante un periodo, como es la comida, el agua…
SECCION 3: VIVIR FUERA DE LA TIERRA
6-Los astronautas están lejos de las tiendas, por lo que dependen de suministros periódicos de alimentos. Cada pocos meses una nave espacial automatizada, como el Vehículo Automatizado de Transferencia de la ESA o la nave rusa Progress, llega cargada con frutas frescas, agua y comidas envasadas.
Los alimentos espaciales se conservan enlatados o envueltos en papel de aluminio
7-Sacar la basura en el espacio no es tan fácil como lo hacemos en casa. Los astronautas no pueden coger una bolsa, abrir la puerta y arrojarla fuera. En cambio, deben cumplir un estricto proceso recolección, clasificación y posterior eliminación de los desperdicios. En este sentido, la Estación Espacial Internacional (ISS) acaba de probar un nuevo método que promete ser más “eficiente y sostenible”.
En la actualidad, la ISS almacena durante meses la basura recolectada, a la espera de la llegada de la próxima misión no tripulada con suministros. Una vez que la cápsula de carga ha sido vaciada, los astronautas pueden colocar las bolsas de basura dentro de ella para que se quemen en la atmósfera terrestre. ¿El problema? Estas misiones suelen retrasarse, por lo que la basura empieza a acumularse.
8-La comunicación se logra principalmente por medio de ondas de radio entre el espacio y la Tierra, que son transmitidas gracias a una red de antenas en todo el mundo junto con satélites.
El sistema en tierra que supervisa el vuelo espacial interactúa directamente con la computadora de la nave y, al mismo tiempo, con los astronautas. Para eso se emplean equipos de radio especialmente diseñados para este propósito, los cuales deben trabajar con muy buena fiabilidad y con el mínimo de interferencia posible para evitar errores que pueden ser fatales
9-El Lunar Roving era un rover lunar todoterreno empleado por los astronautas de las misiones Apolo 15, 16 y 17 en sus desplazamientos por la superficie lunar.
Para llevar el rover lunar a la Luna, los astronautas utilizaron el Modulo Lunar (LM) que los llevaba desde la nave de comando hasta la superficie lunar.
Puede ser controlado de forma remota, contiene sistemas diseñados para funcionar en un ambiente extremo
English translation
SECTION 1: MY SPACE CAMP
1- In the project we have different phases, at the beginning we did an initiation in Tinkercad to learn how to handle the application and from there we have created different objects helping us with YouTube videos that told us the measurements, the objects… And among them we have done a lunar robe, a lunar greenhouse, an astronaut, a rocket and habitable modules to then put everything together and create a lunar camp for astronauts so that they can continue living, researching the moon…
We have also been doing readings through websites with content about the moon, trips to it, how to survive in space, how to build… and then we had to answer some questions about that topic and we had to get the answers from the website .
SECTION 2: BUILD A SPACE CAMP
3- Surely the space camp will be built in the Shackleton crater at the south pole of our satellite, because it is almost constantly illuminated and there is water ice in the crater. The base is on the surface, which will greatly simplify construction. It will be covered with a layer of soil.
4-The inhabitants of the Moon would have to build buildings with walls thick enough to block the entry of radiation and wear cumbersome space suits every time they go outside.
These considerations mean that when we expand the first bases and begin building structures on the Moon, the lunar concrete, which is a mixture
of sulfur and aggregate (grain or crushed rock; normal concrete is aggregate, cement, and water) may be a good option.
5- Because they have all the needs that satisfy them to be able to live for a period, such as food, water…
SECTION 3: LIVING OFF EARTH
6-Astronauts are far from stores, so they depend on regular food supplies. Every few months an automated spacecraft, such as ESA’s Automated Transfer Vehicle or the Russian Progress spacecraft, arrives loaded with fresh fruit, water and packaged meals.
Space foods are preserved in cans or wrapped in aluminum foil.
7-Taking out trash in space is not as easy as we do it at home. Astronauts cannot pick up a bag, open the door and throw it outside. Instead, they must comply with a strict waste collection, classification and subsequent disposal process. In this sense, the International Space Station (ISS) has just tested a new method that promises to be more “efficient and sustainable.”
Currently, the ISS stores the collected garbage for months, waiting for the arrival of the next unmanned mission with supplies. Once the cargo capsule has been emptied, astronauts can place the garbage bags inside it to burn in Earth’s atmosphere. The problem? These missions are often delayed, so the trash starts to pile up.
8-Communication is achieved mainly through radio waves between space and Earth, which are transmitted thanks to a network of antennas around the world along with satellites.
The ground system that supervises space flight interacts directly with the ship’s computer and, at the same time, with the astronauts. For this, radio equipment specially designed for this purpose is used, which must work with very good reliability and with the minimum possible interference to avoid errors that can be fatal.
9-The Lunar Roving was an all-terrain lunar rover used by the astronauts of the Apollo 15, 16 and 17 missions in their movements on the lunar surface.
To take the lunar rover to the Moon, the astronauts used the Lunar Module (LM) that took them from the command ship to the lunar surface.
Can be controlled remotely, contains systems designed to operate in an extreme environment
#3D Design
Other Projects