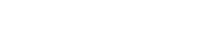Saros by Saros
郑州轻工业附属中学 河南省郑州市-河南省 China 19 years old 4 / 1 English Mars
Project description
Our Mars settlement project aims to develop human habitats on the Martian surface, providing long-term accommodation solutions for Mars exploration and space travel. The project will utilize the latest space technologies while emphasizing the sustainable development of the camp to reduce dependence on Earth’s resources.
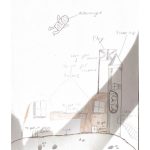
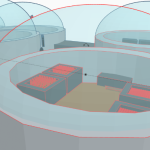
Site Selection: Marbahi Crater in the Utopia Planitia region
Reason: It is located in a low-latitude area with minimal diurnal temperature variation and abundant sunlight. Additionally, the atmosphere is relatively thick.
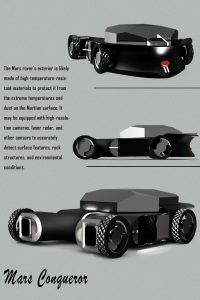
Camp Construction: We will employ directional blasting to create the camp within the mountain, followed by covering the surface with Martian soil to shield against radiation.
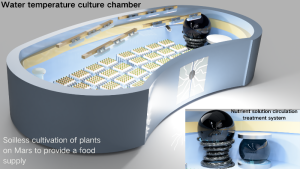
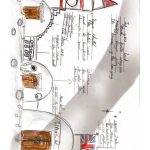
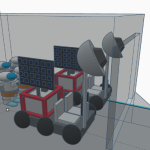
Food: Aquaponic greenhouses for fish farming and environmental control systems for crop cultivation. Later stages involve simulating Earth’s plant growth environment, optimizing and purifying Martian soil, and adding organic matter to meet plant growth requirements. A Martian biolab centered around plant genetic technology will be established based on synthetic biology.
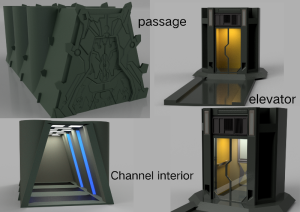
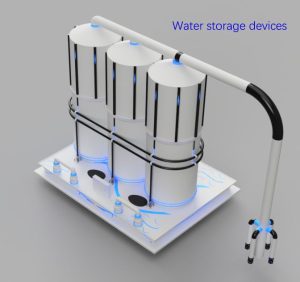
Water: Utilizing the “Rodriguez Well” principle, a drilling machine will penetrate the surface to reach the ice layer below, continuously pumping heat into the underground water reservoir to gradually form a water reservoir and a sustainable water supply system.
Oxygen: Following the MOXIE experiment’s approach, we will collect and utilize the abundant carbon dioxide in the Martian atmosphere to produce oxygen resources.
Power: Solar energy (thin-film photovoltaic modules paired with trough or pyramid-shaped static concentrators)
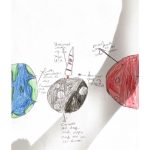
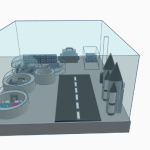
Camp Positioning: Primarily for scientific research on sustainable development, Martian resources, and nuclear power. Secondarily, for commercial purposes such as building hotels to experience Martian life and transporting scarce resources to Earth.
A Day in the Life of an Astronaut:
Morning:
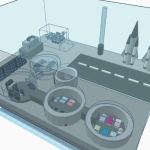
Routine habitat maintenance, including checking life support systems, energy supply, and communication equipment.
Scientific experimentation time, where astronauts will conduct various research activities in the laboratory, such as analyzing collected Martian rock and soil samples.
Afternoon:
Engage in outdoor activities such as driving Mars rovers, geological exploration, or installing experimental equipment.
Conduct space environmental monitoring, collect data, and analyze it.
Evening:
Perform daily cleaning and tidying tasks to ensure the camp’s cleanliness.
Pre-bedtime checks to ensure all systems are functioning properly, then rest to prepare for the next day’s tasks.
Project video
#
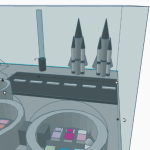
3D Design
Other Projects
Alhaurín de la Torre – Spain
Habitats in space – Drawings of their designs
stockton – United Kingdom