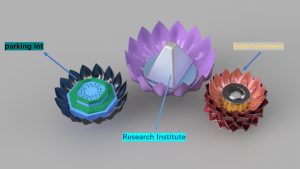
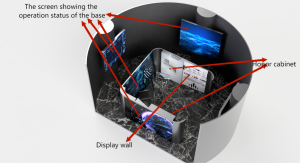
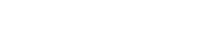5.1 – What would you include in your astronaut training programme, to help prepare the astronauts for a Moon mission?
Training content:
Physics and Aerospace Technology: Learn and master knowledge of spacecraft design, construction, control and flight, and understand common physical phenomena in vacuum, low gravity, etc.
Space Adaptation: Understand the effects of space environment on human body, including space sickness, radiation damage, etc., and learn coping strategies.
Emergency Rescue and Self-Protection: Learn how to deal with critical situations during space flight, including fires, storms, mechanical failures, etc.
Robotics and Automation Technology: Understand the application of robotics and automation technology in space, including operating and maintaining robot systems.
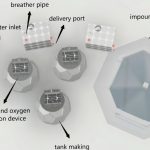
Vehicles and Life Support Systems: Learn how to operate spacecraft and lifesupport systems in space, including gas management, water circulation, constant temperature and humidity, etc.
Mental and Psychological Health: Cultivate the ability of astronauts to maintain a positive mentality and mental health in environments of loneliness, stress and uncertainty.
Simulation training: Help astronauts adapt to space life and improve their ability to handle various tasks through simulating space environment and tasks.
Extravehicular Activities: Learn the operation and safety regulations of extravehicular activities, including spacewalking, space missions, etc.
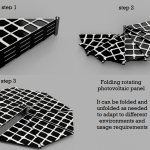
5.2 – What space vehicles will your future Moon mission need? Describe the vehicles found in your Moon camp and consider how you will travel to and from Earth, and explore new destinations on the Moon’s surface.
Future lunar missions require a durable and efficient spacecraft capable of carrying large amounts of cargo and personnel, and conducting exploration and scientific experiments on the moon’s surface. This spacecraft should be reusable to reduce costs and increase efficiency.
In the lunar base, there are many large vehicles that can travel on the moon’s surface to transport personnel and cargo. These vehicles can be modified into scientific laboratories or mobile living quarters for long-term stays on the moon’s surface.
To travel between Earth and the moon, future spacecraft require sustainable energy supplies and highly automated technology to ensure safe and reliable navigation. Additionally, this spacecraft should have the ability for rapid deployment and assembly so that it can depart quickly when needed.