Moon Camp Pioneers Gallery 2020-2021
In Moon Camp Pioneers each team’s mission is to 3D design a complete Moon Camp using Fusion 360. They also have to explain how they will use local resources, protect astronauts from the dangerous of space and describe the living and working facilities.
Team: Hexagon
DLR_School_Lab TU Dresden Dresden Germany 15, 16
External viewer for 3d project
|
Project description
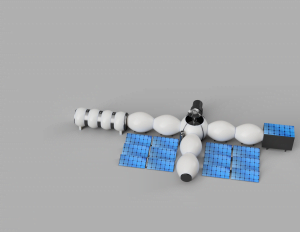
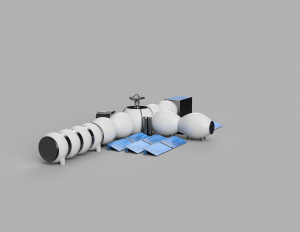
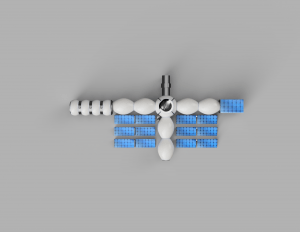
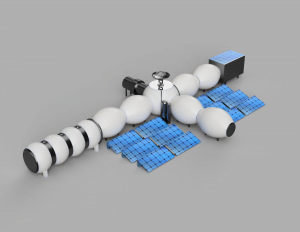
The Moon Camp looks like a cross. Every part of the Moon Camp is connected with the centre, so every spot is accessible from any other spot in the camp. This way, the astronauts don’t have to leave the inside of the Moon Camp as often. Besides, they walk less to get from point A to point B than they would if the Moon Camp was a straight line. The Camp consists of a sleeping and eating area, a double door system connecting the camp with the outside of the Moon, a scientific section, a greenhouse, a workshop, a device for measuring radio waves, and a combination of photovoltaic and solarthermics. |
|||
|
Where do you want to build your Moon Camp?
The camp would be constructed at the opposite site of the Moon to capture radio waves, undisrupted by any radio waves sent from Earth [1]. The part of the camp, where the crew lives, is optimally built in safe environment like crater to be protected from comets and other stuff coming from space [2]. Big craters are found at the poles of the Moon [2]. It’s even more beneficial to settle down at a pole, because there is a relatively large amount of Moon ice [3], which can be investigated first and used later for fuel cells [4] or hydrogen production [5]. [1] Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt: Erde und Mond. 2020. p. 103. URL: https://www.dlr.de/next/Portaldata/69/Resources/downloads/ErdeMond_05_gesamt150dpi.pdf [accessed on 20.04.2021] [2] Nadia Drake: Why the moon’s south pole may be the hottest destination in space. 2019. URL: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/science/article/why-moons-south-pole-may-be-hottest-space-destination-blue-origins-shackleton-crater [accessed on 20.04.2021] [3] NASA: Ice Confirmed at the Moon’s Poles. 2018. URL: https://www.nasa.gov/feature/ames/ice-confirmed-at-the-moon-s-poles [accessed on 20.04.2021] [4] Martin Rosenberg / Martin Gent / Wiebke Ziegler: Brennstoffzelle. 2021. URL: https://www.planet-wissen.de/technik/energie/brennstoffzelle/index.html [accessed on 20.04.2021] [5] U.S. Department of Energy: Hydrogen Production: Electrolysis 2021. URL: https://www.energy.gov/eere/fuelcells/hydrogen-production-electrolysis [accessed on 20.04.2021] How do you plan to build your Moon Camp? Describe the techniques and materials you would use.
The Moon Camp looks like a cross. Every part of the Moon Camp is connected with the centre, so every spot is accessible from any other spot in the camp. This way, the astronauts don’t have to leave the inside of the Moon Camp as often. Besides, they walk less to get from point A to point B than they would if the Moon Camp was a straight line. The Camp consists of a sleeping and eating area, a double door system connecting the camp with the outside of the Moon, a scientific section, a greenhouse, a workshop, a device for measuring radio waves, and a combination of photovoltaic and solarthermics. All main components are inflatable in order to make the transport from the earth to the moon easier by reducing the weight. The environment on the Moon is very dangerous for the astronauts. Explain how your Moon Camp will protect them.
The part of the camp, where the crew lives, is optimally built in safe environment like crater to be protected from comets and other stuff coming from space [1]. Big craters are found at the poles of the Moon [1]. [1]Nadia Drake: Why the moon’s south pole may be the hottest destination in space. 2019. URL: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/science/article/why-moons-south-pole-may-be-hottest-space-destination-blue-origins-shackleton-crater[accessed on 20.04.2021] Explain how your Moon Camp will provide the astronauts with:
|
|||
|
Water
|
Food
|
Electricity
|
Air
|
|
It’s even more beneficial to settle down at a pole, because there is a relatively large amount of Moon ice[1], which can be investigated first and used later for fuel cells[2] or hydrogen production[3]. [1] NASA: Ice Confirmed at the Moon’s Poles. 2018. URL: https://www.nasa.gov/feature/ames/ice-confirmed-at-the-moon-s-poles [accessed on 20.04.2021] |
Food supply for the astronauts on the Moon is one of the biggest challenges. It must be taken into account that the food is both balanced and adequate. All necessary vitamins, proteins, carbohydrates, fats and minerals must be provided. Since breeding animals is excluded, everything must be obtained mainly from fruits and vegetables. However, it should also be noted that on the Moon there is not much water, good soil or microorganisms to improve it. Therefore, only plants with very low growth requirements can be grown. First of all, we checked the vital vitamins and nutrients of a human. All those vital vitamins and nutrients are obtained from the following plants: cucumber, kohlrabi, mushrooms, chickpeas and leien (flax). In Antarctica, experiments have already been carried out to grow plants under extreme conditions similar to those on the Moon [1]. Cucumber and kohlrabi grew there successfully and provide the vitamins A, B, C, E, K, I, J. Mushrooms and chickpeas provide the missing vitamins D, F and G. They also have very low growth requirements, which make it possible to let them grow on the Moon. Finally, flax could be an option, too, because it provides flax seeds, which contain many nutrients and could be processed to oil. In fact, oil is important to lead a balanced diet. To get sufficient quantities of vitamin B-12 and vitamin D the astronauts should also use substitute products. In addition, the intake of protein powders will be unavoidable, because they are very important for muscle building[2]. The structure of the greenhouse is similar to that of most modules of our Moon station and consists of contiguous inflated segments with intermediate floors for stabilization and better spatial distribution. In the greenhouse there will be rows of metal shelves where the plants grow. The principle of “Aeroponics” is used. The advantage is that no earth is used, which couldn’t be taken to the Moon anyway. The principle works as follows: the roots are sprayed with nutrient containing water and the leaves are illuminated with LED lamps. The air is enriched with CO2, germs and fungi are filtered out. One disadvantage is the high energy consumption, caused by the lamps[1]. [1] Tanja Zech: Gemüse aus dem ewigen Eis deutsche Forscher wollen in der Antarktis Gemüse anbauen. Verrückte Idee? Keineswegs! Das ist der Sinn des Projekts. 2018. URL:https://www.deutschland.de/de/topic/umwelt/eden-iss-gewaechshaus-in-der-antarktis [accessed on 20.04.2021] |
One of the most important issues on the Moon is energy. Since neither wind nor liquid water or fuels like coal etc. exist on the Moon, the Sun is the only sustainable source of energy. That’s why in our design sketch solar cells are placed next to the camp to produce electricity. Since the power generation by the solar cells varies greatly throughout the day, an accu is connected to the grid to reduce the power surplus at the Moon day and to store the energy. To store the energy for a longer period of time, a reversible fuel cell is connected to the grid, which divides the water into oxygen and hydrogen when there is a surplus of energy or the other way around when more electricity is needed at night, for example, to generate electricity from oxygen and hydrogen. We have chosen the fuel cell because it can store a lot of energy with little water. To use the solar energy completely, we have constructed a solar thermal system in addition to the solar cells. The black solar collectors are placed between the solar cells. |
The air which is needed for the astronauts is provided by the earth and must be transported every now and then with supply rockets from the earth to the moon to refresh the air in the camp. |
|
Explain what would be the main purpose of your Moon Camp (for example: commercial, scientific, and/or tourist purposes).
This Moon Camp shall be mostly used for scientific purposes. |
|||
|
Describe a day on the Moon for your Moon Camp astronaut crew.
A daily routine in this Moon Camp could be like this: after getting up at a regulated time the crew starts the day by eating breakfast. Work begins afterwards, which is for instance composed of examining materials found on the Moon, evaluating data, exploring the Moon by expeditions, communicating with Earth and much more. In between the work the crew eats a few more times and does much sport to stay in shape. When work is over the astronauts have several hours of free time and after being up for fourteen to sixteen hours, they go to bed even though the light is still the same as when they got up, because the days on the Moon are quite long, especially at one of the poles [1]. A controlled daily routine is important for the crewmembers to get enough sleep. [1]P. Gläser / J. Oberst: Illumination conditions at the lunar poles: Implications for future exploration. 2017. URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0032063317300478?via%3Dihub [accessed on 20.04.2021] |
|||