Moon Camp Pioneers Gallery 2021-2022
In Moon Camp Pioneers each team’s mission is to 3D design a complete Moon Camp using Fusion 360. They also have to explain how they will use local resources, protect astronauts from the dangerous of space and describe the living and working facilities.
Team: Space Bound
Bertrand Russell College Krommenie Netherlands 18 2 / 2
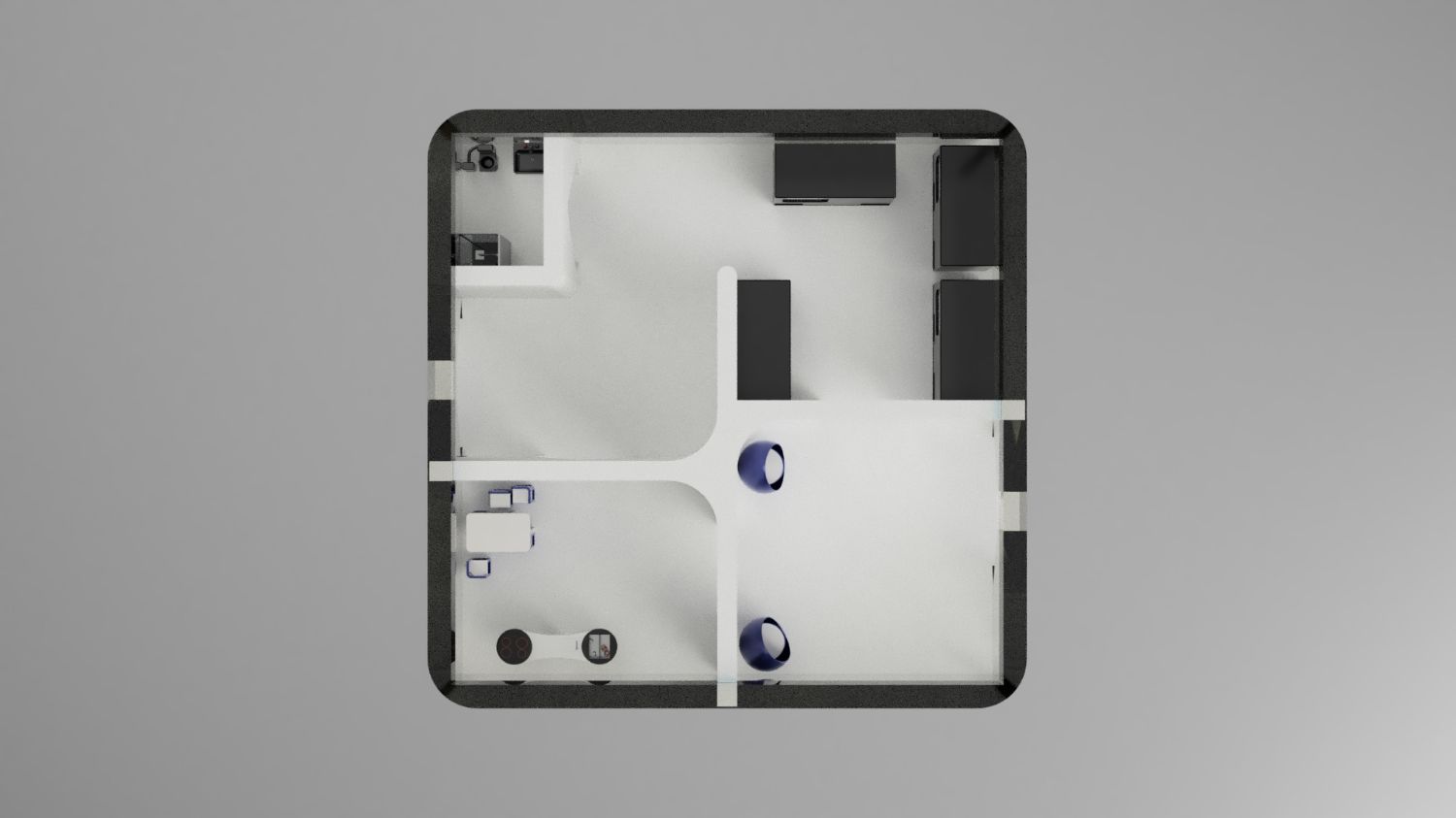
External viewer for 3d project
|
Project description
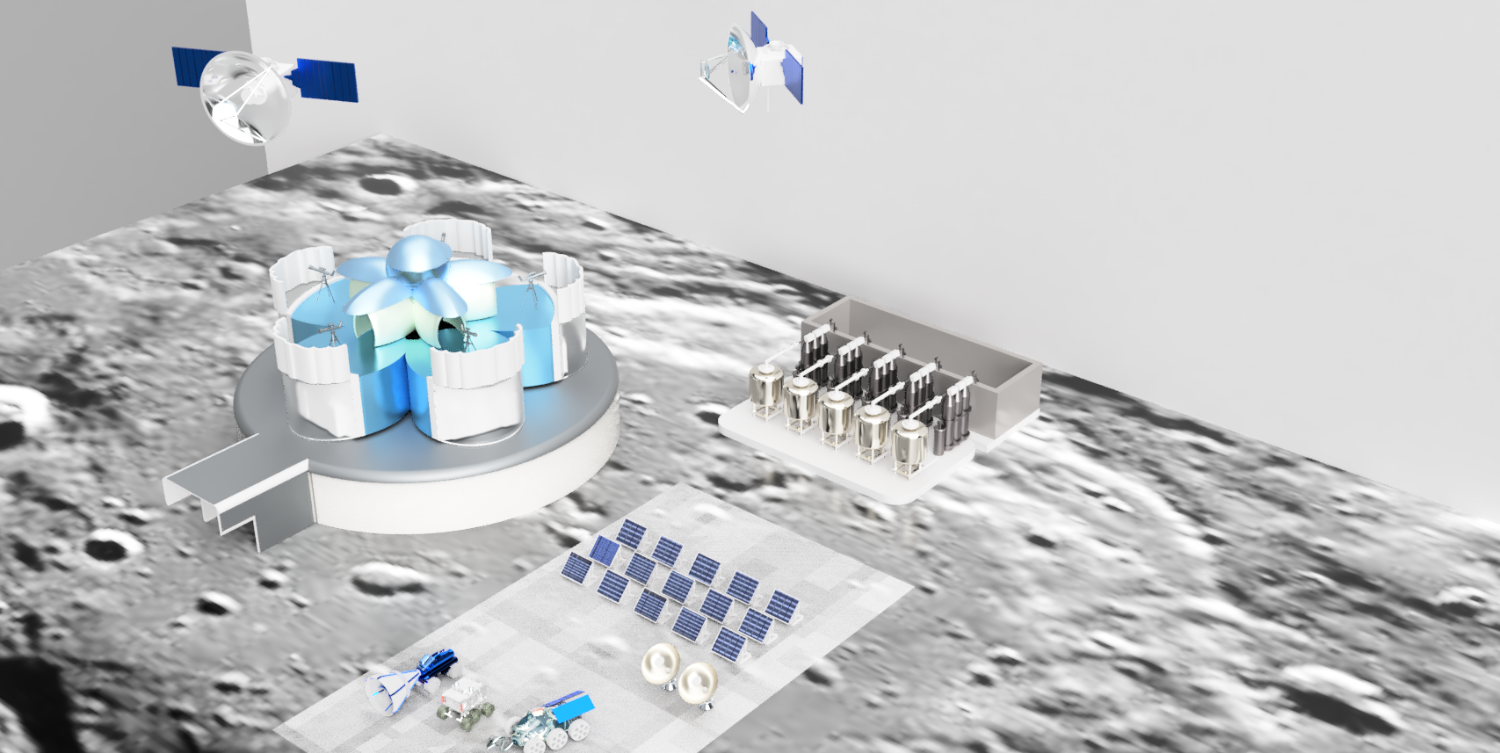
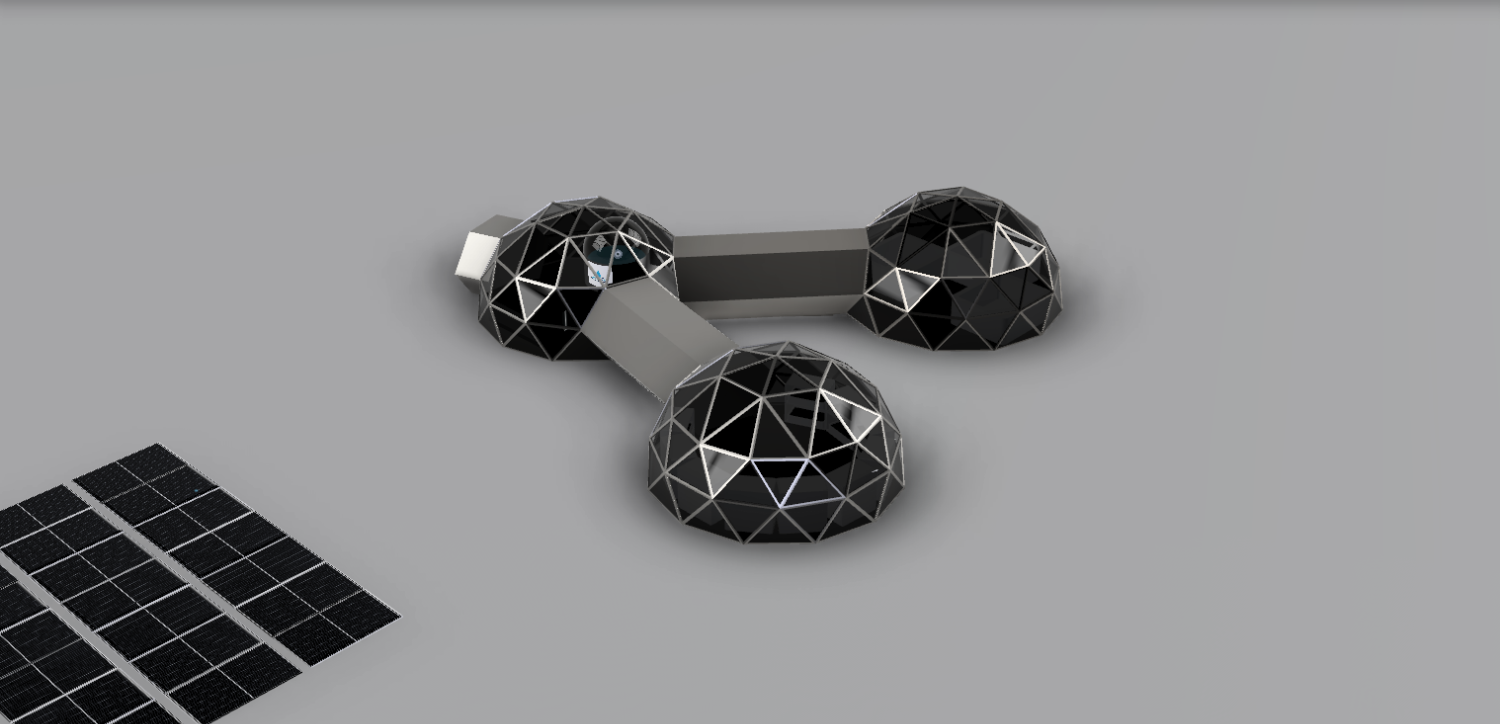
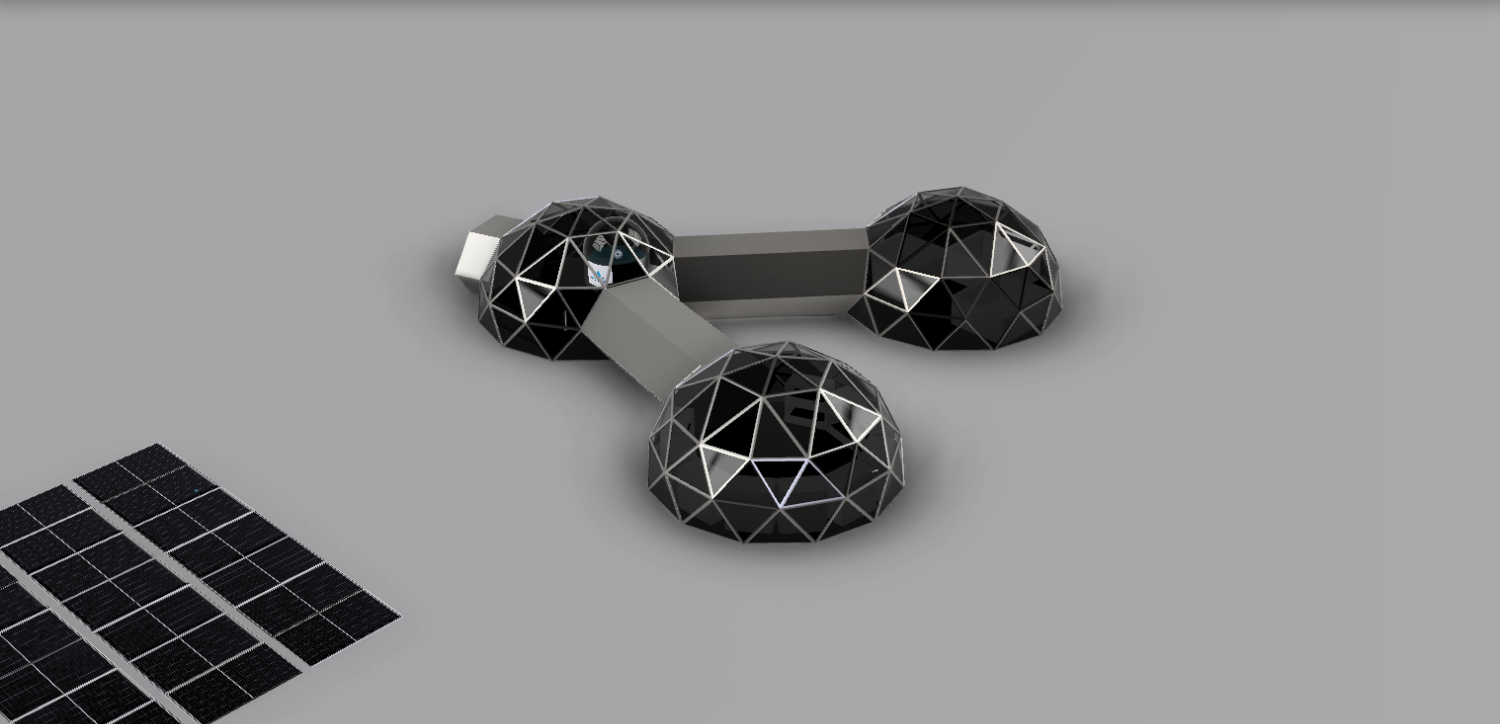
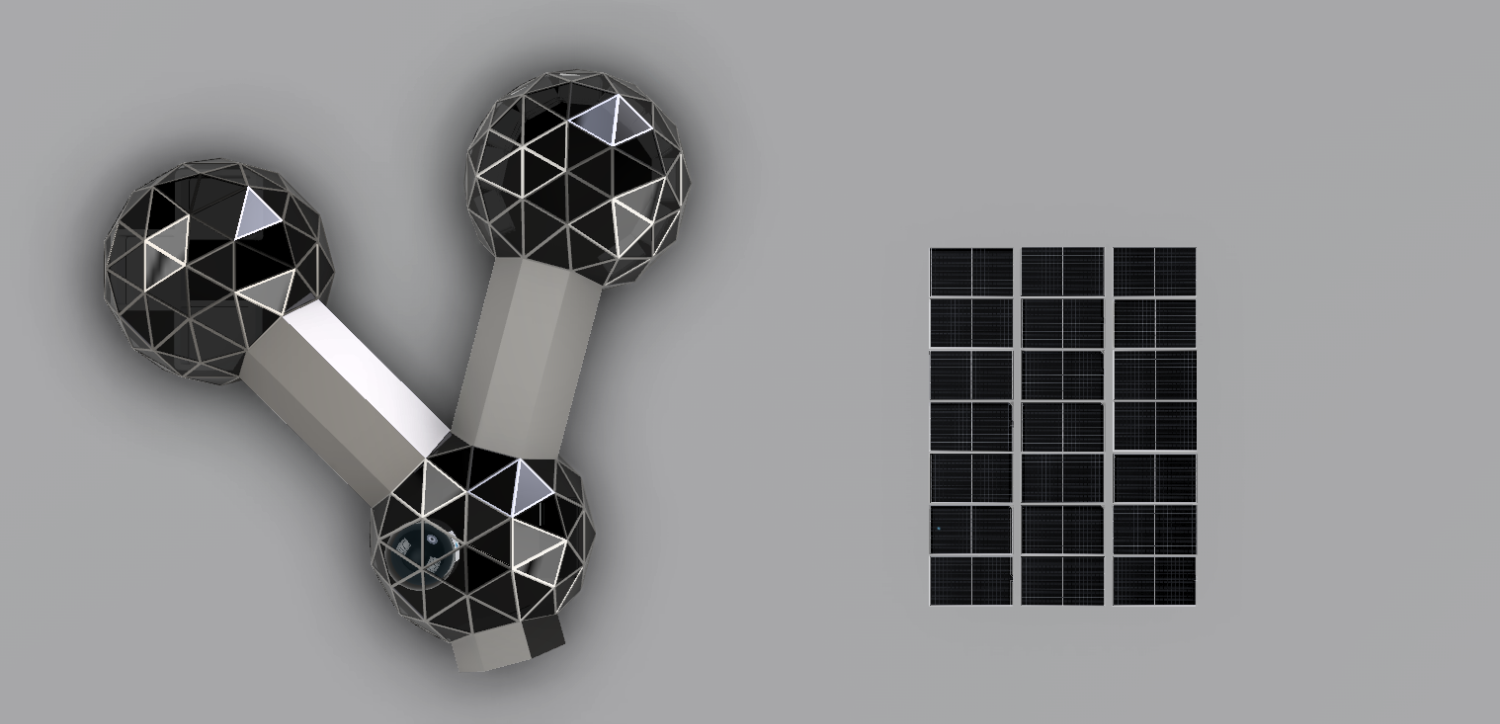
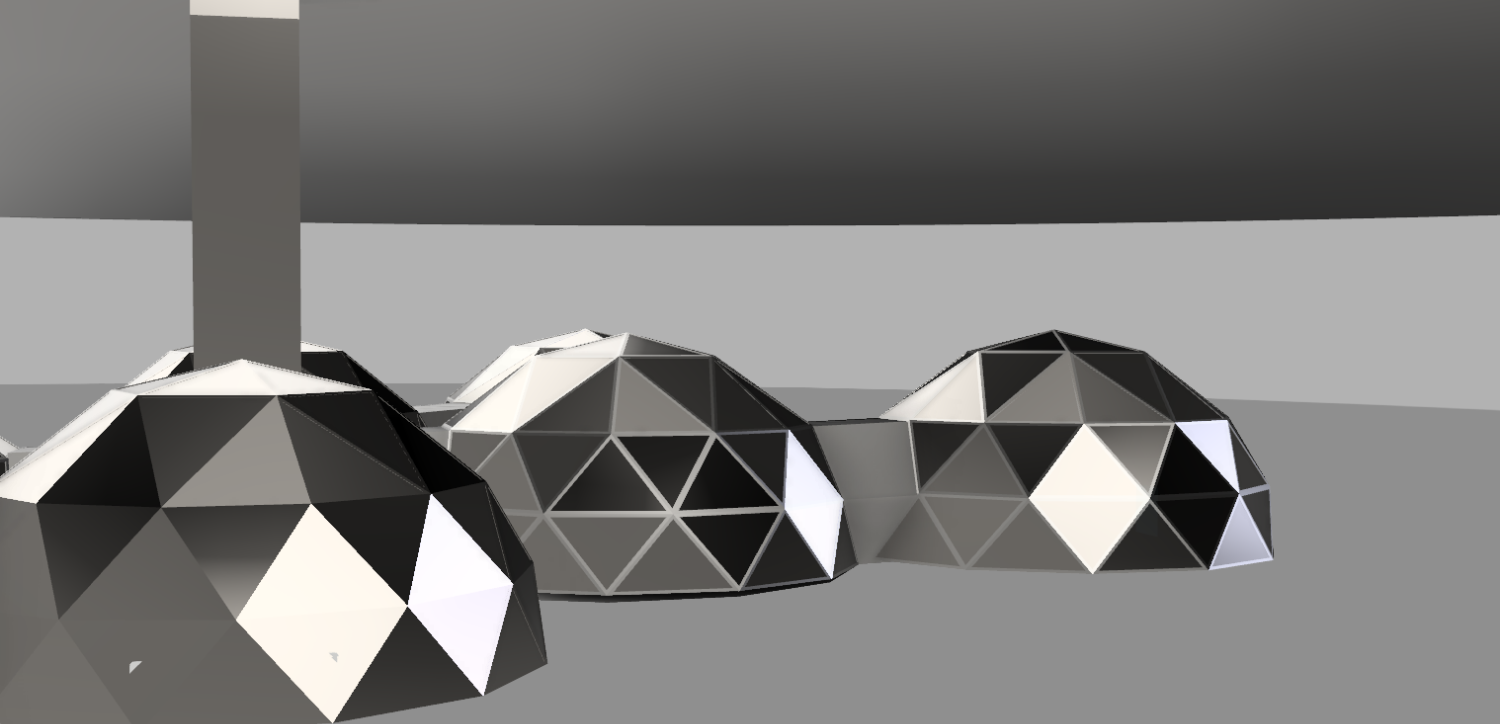
With this project we emphasise the importance of a moon camp being self-sufficient. This will set an example for the earth. The moon base will be mainly for research. Besides research on the development of organisms under the conditions on the moon, there will also be research on lunar soil. This will provide us with a broader perspective on the development of organisms and conditions in space. This will help develop space travel in the future. The team of astronauts will consist of 6 people. Upon arrival, the astronauts will bring their own food and resources, in the future the moonbase will be self-sufficient. The astronauts will maintain the earth’s day-night rhythm. During the day, they will split into two groups to carry out their research and tasks. Because of this, there will always be astronauts awake to manage the moon base. During the day the astronauts come together several times to reflect on their progress. Most of our moonbase will be built on earth, following the same path as ISS. The moonbase will consist of strong and lightweight geodomes. We chose the triangle structure because the dome does not require any internal support and the triangles distribute the weight evenly over the structure. The domes will be placed on the south pole of the moon which is constantly illuminated. The moonbase will be partly underground and partly above ground. |
|||
|
2.1 Where do you want to build your Moon Camp?
We chose to place our moon camp on the moon’s south pole, on the rim of the Shackleton crater. This will be a functional place to live, work and perform research. The crater’s rim is exposed to almost continual sunlight. We will place our solar panels there. The inside of the crater is always in the dark and is extremely cold. Some studies show that there is ice in those parts of the krater. These resources offer many advantages for the necessities of life. Most importantly a secure source of electricity and water. Because of that the moon base will eventually be completely self-sufficient. The temperature in this region is more stable which will be useful for potential outside work. Inside our moon camp, we will create our own pleasant climate. Most of our base will be underground. This way the astronauts will be protected from meteorites and radiation. 2.2 How do you plan to build your Moon Camp? Describe the techniques, materials and your design choices.
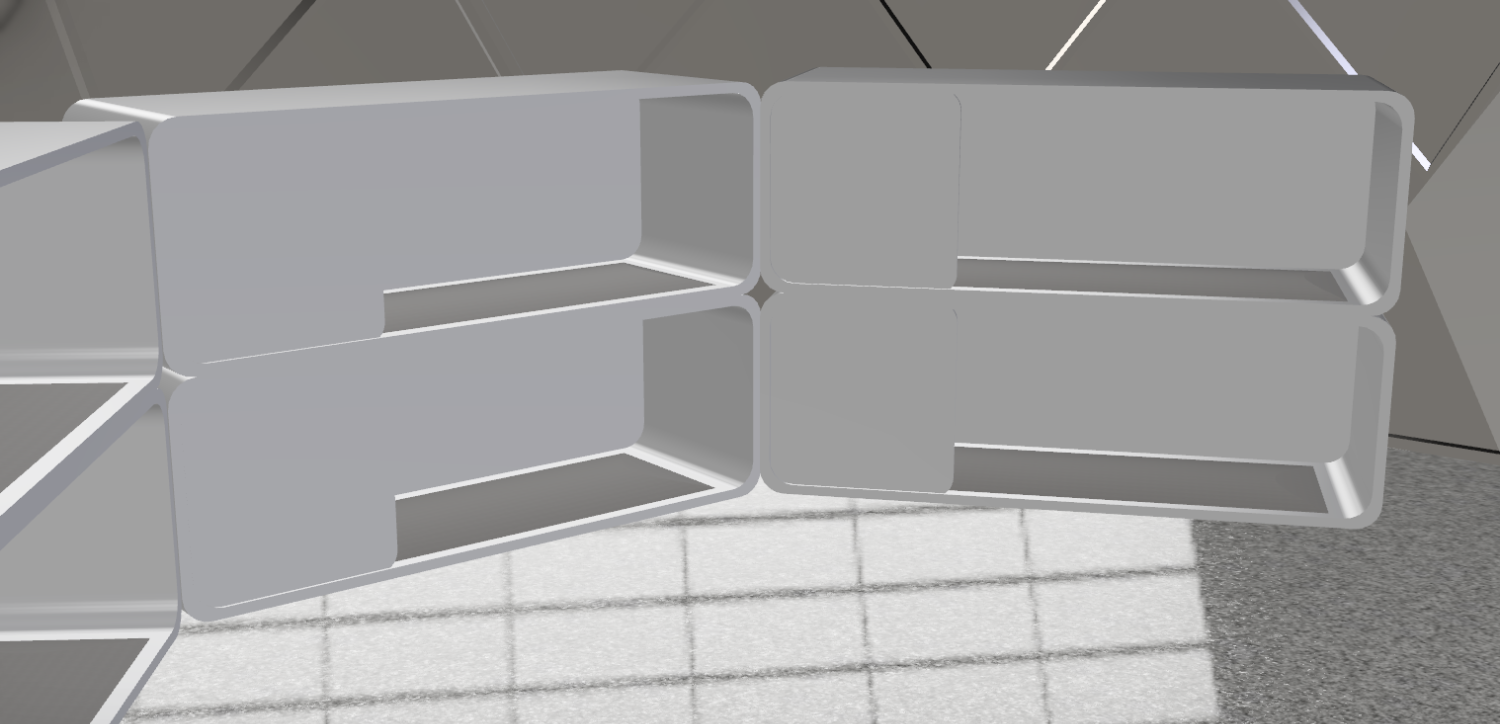
The base will be partly underground and partly above ground and consists of geodomes. The crew will mostly live and do research underground. Due to the moon sand on top in combination with the demron on the inside of the moon base, the crew will be better protected against radiation and meteorites. The lunar base has an above-ground entrance that contains a cleaning system for suits and equipment so that no moon sand gets into the base. For safety, there are emergency exits from each underground compartment. Before the astronauts come to the moon, robots will dig the holes for the underground part. Most parts will be built on earth, following the same path as ISS. Those parts will be transported to the moon and will be assembled by the astronauts assisted by robots. In the first stage of the mission, the astronauts will live in the rocket they came in. In the second stage, the base will be finished, and the astronauts will move there. The walls will be made of a double layer of titanium with aerogel isolation mats in between. Titanium has a favourable strength-to-mass ratio. Aerogel is a very good isolator and is lightweight. For the windows, we will use transparent silicate fibreglass. Because of these materials and the shape, consisting of triangles, the structure will be lightweight and strong. This will be useful when the parts of the moon base will be transported from earth to the moon. 2.3 The environment on the Moon is very dangerous for the astronauts. Explain how your Moon Camp will protect them. (maximum 150 words)
When making the design choices we took into consideration: moon sand, landscape, radiation, meteorites, and temperature. The base will be completely sealed and will have entrances with cleaning systems so none of the dangerous moon sand will enter. To make sure the astronauts know the landscape, a topographical elevation map of the moon will be made. The walls of the base will be made of titanium because it is strong, lightweight and can withstand extreme temperatures. We will use aerogel matts with a thermal conductivity between 0,0135 and 0,017 W/m K. The base is therefore protected against meteorites and extreme temperatures. Demron is a radiation shielding material and will be placed on the inside of the base. It has slightly lower radiation protection than lead shielding, but it is flexible and lightweight. The underground part of the moon base is covered with lunar sand, also protecting the base from radiation. |
|||
|
2.4 Explain how your Moon Camp will provide the astronauts with:
|
Water
|
Food
|
Power
|
Air
|
|
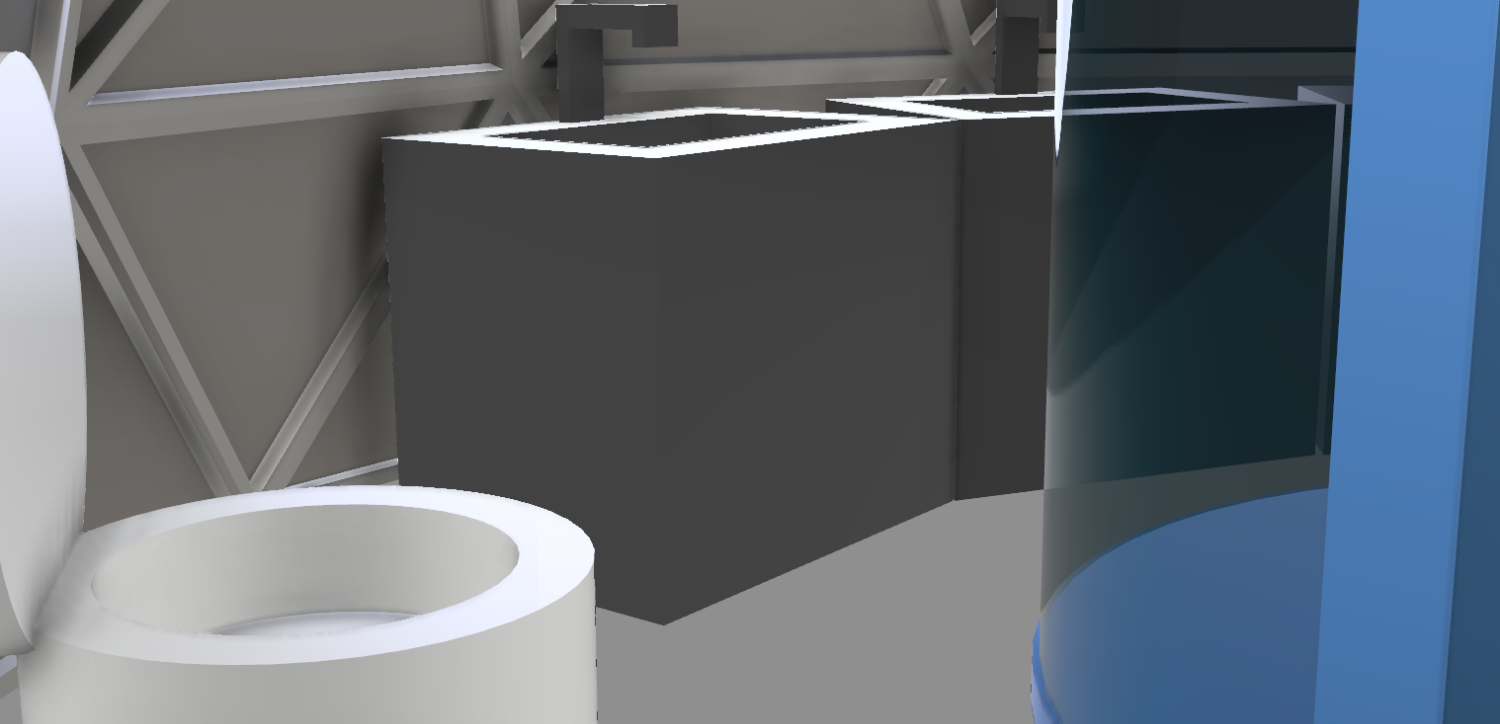
To generate water ISS used a water recovery system. This is a part of the environmental control and life support system onboard of ISS. The water is collected within ISS. They provide clean water by recycling the crew’s urine, sweat, other condensates in the cabin and wastes produced due to extravehicular activity. This water is filtrated and can be used as drinking water or water for plants. |
At the beginning of the mission, the astronauts will eat the food taken from the earth. Later on, they can eat the vegetables from the greenhouse. The crew will mostly live on a plant-based diet. Consisting of soy, legumes, corn, spinach, potatoes and fruit for a varied diet. These crops will be grown in a closed greenhouse with artificial light, where the plants are protected from radiation. |
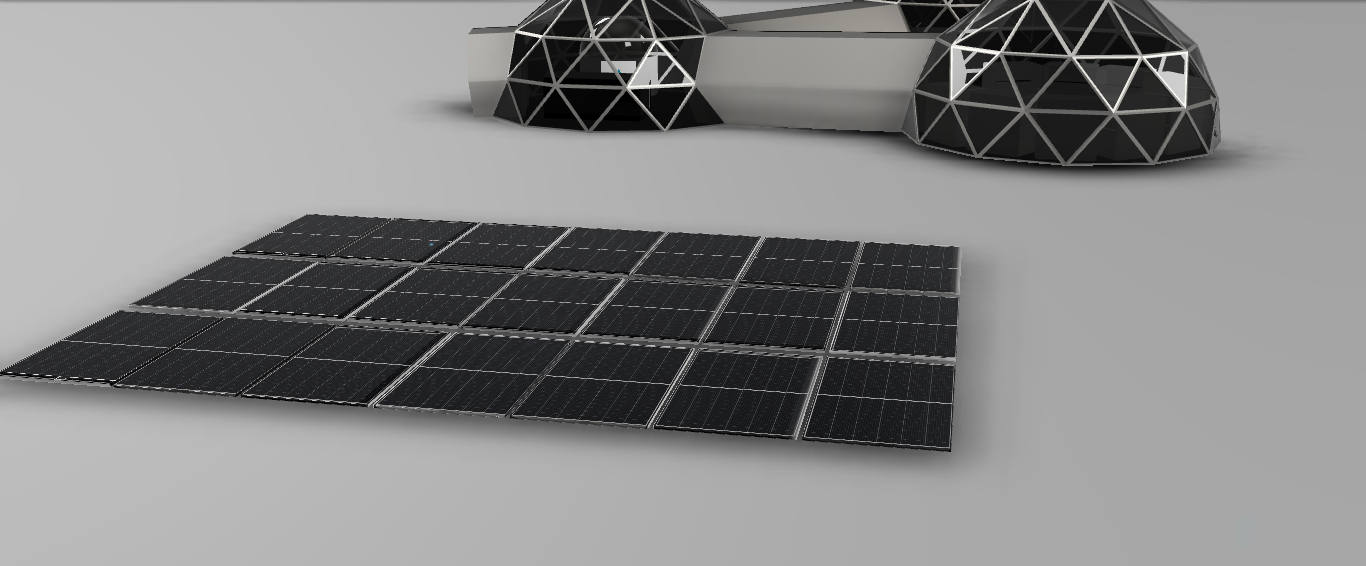
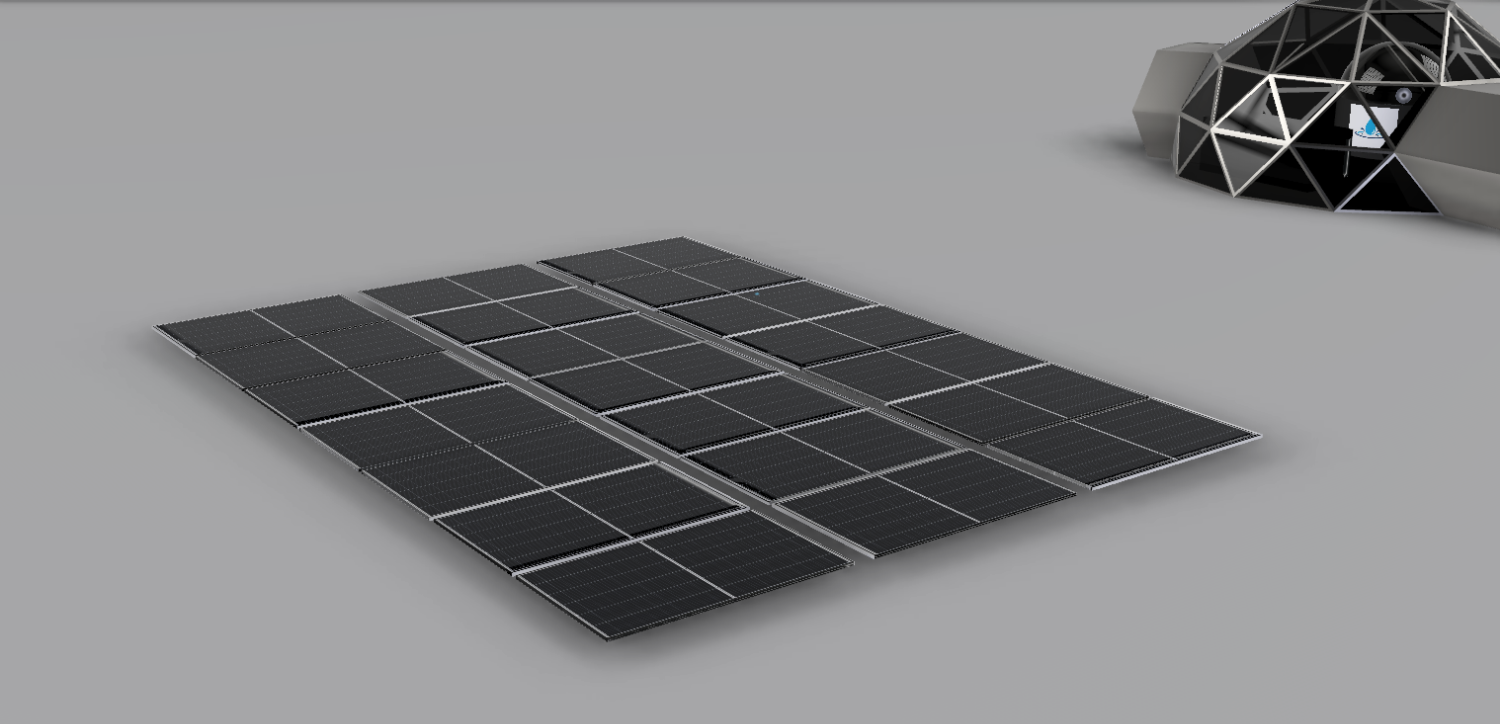
The main source of electricity will be produced by solar panels. They will be placed on top of the Chakleton krater which is constantly illuminated, therefore there is a constant source of electricity. The surplus of electricity is stored in large batteries. This is useful if there is a shortage of energy and if the solar panels do not work. With that, the base will never have a shortage of electricity. With electrolysis of water rocket fuel (hydrogen and oxygen) will be created. This can also serve as an energy reserve. |
To generate the oxygen, we will use the same system used by ISS. There is an oxygen generation system, for the electrolysis of water. An important component is the earlier mentioned water recovery system. This water is used to create breathable air to sustain life on board. On our moonbase not only the water collected within the base will be used, but also the moon ice that is mined will be used. The air will be refreshed with an air filter system. |
|
2.5 Explain what would be the main purpose of your Moon Camp.
The mission to the moon has mainly scientific purposes. First, research into organisms and the effect of the moon on their growth and living processes. We will take animals (like rats, chickens, and bees) and plants to the moon and compare the influences of gravity and radiation on the moon with those on earth. |
|||
|
3.1 Describe a day on the Moon for your Moon Camp astronaut crew.
The place of the moon camp is never in the dark, therefore we can not create a ‘natural’ day-night cycle on the moon. Because of that, the astronauts will follow the earth’s day-night cycle. This will also be easy for communication with earth, and since the astronauts on the moon don’t live on the moon permanently it will be easier to adjust to living on earth again. The moon base crew will consist of 6 people, divided into two groups. For safety, the two groups will never sleep at the same moment. There will always be three people awake to notice and solve potential problems. The first group sleeps from 20.00 till 3.00 o’clock. The second group sleeps from 3.00 till 10.00 o’clock. While the second group sleeps the first group has breakfast from 3.00 until 3.45. Thereafter they will sport for one hour to remain strong and have 15 minutes to shower. After that, the astronauts have one and a half hours of free time, they can use this time to hang out in the lounge and call family and friends on earth. From 6.30 until 10.00 o’clock this group will go to work. At 10.00 o’clock the second group will wake up. The crew will then have breakfast together for 45 minutes, they will make a plan for the day and have contact with the base on earth. The second group will sport from 10.45 until 11.45 and then have a shower, while the other group will work. The second group will also go to work after that. From two until three the whole crew will have lunch. During lunch, they will make contact with the base on earth and reflect on the day so far. Until 18.00 the crew will work again. Then the crew will have dinner together and have contact with the base on earth and reflect on the past day. The first group will go to sleep after that, while the second group will work again. At 23.30 this group will eat and have free time until three o’clock. Thereafter this group will go to bed and the other group will wake up. And so the day-night cycle will begin again. |
|||