Moon Rover – Building a solar powered rover
In this activity, students will compare the advantages and disadvantages of renewable energy sources and non-renewable energy sources and study simple electrical circuits.
Using the Moon as context, students will build a small motor and a solar cell. They will also identify the main features their rover must have in order to go to the Moon, and improve their inital rover design.
Learning Objectives
Age range:
8-14 years old
Time
Lesson: 1 hour 30 minutes
Resource available in:
Activity 1: Powering a Lunar Rover
In this activity, students learn about the advantages and disadvantages of renewable sources of energy. They will learn about the Moon environment and consider which is the best power source for a lunar rover. The students will also sketch simple electrical circuits.
Equipment
Activity 2: Build a Solar-powered Rover
In this activity, pupils will build a solar-powered rover using a solar cell, a motor, and craft supplies.
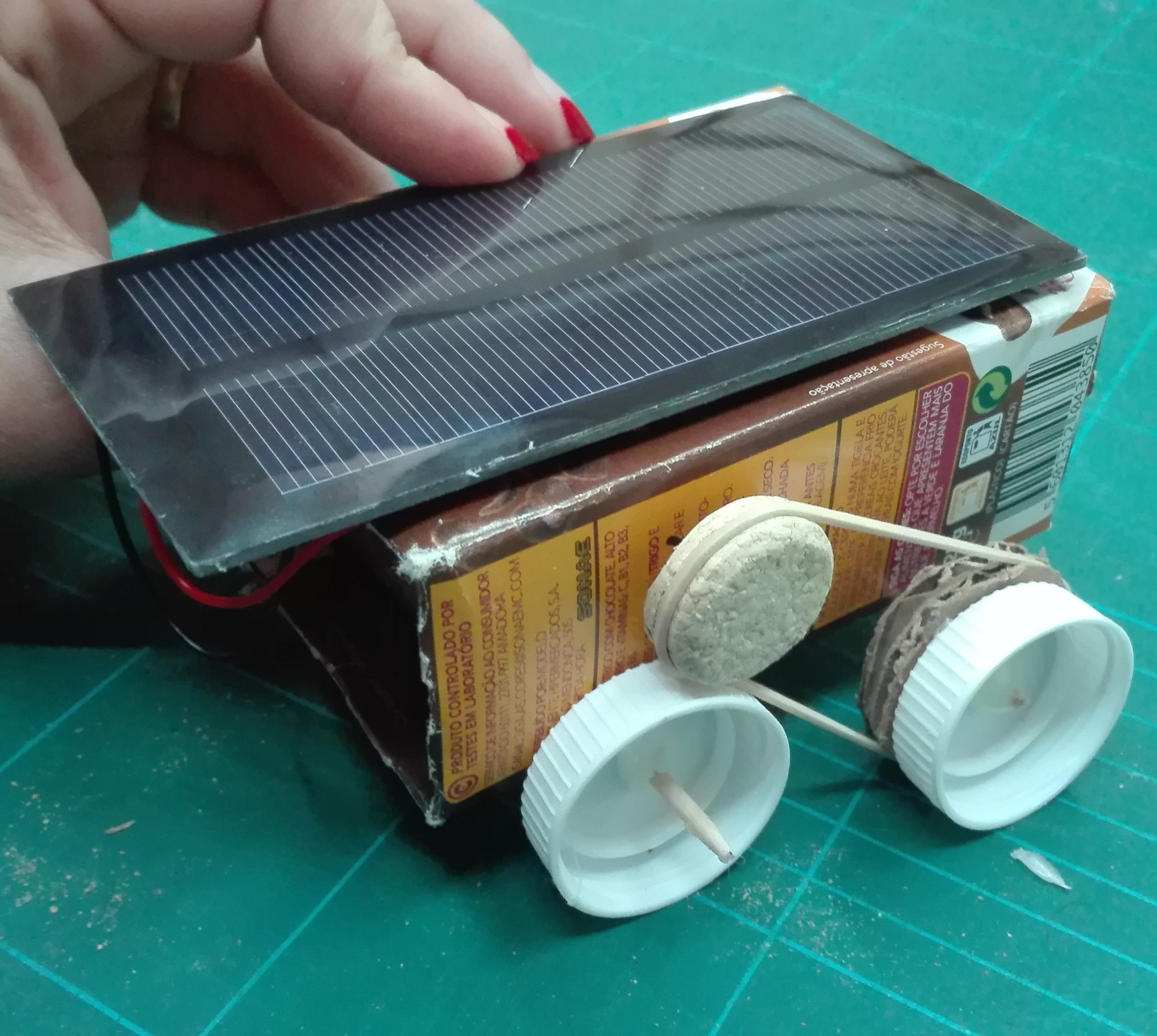

Equipment
Did you know?
A Moon rover will have to be designed to travel to unfamiliar rocky terrain, covered with regolith and with unkown slopes. The rover should have specially designed wheels that can overcome these conditions wihtout having any problems. It will also have to carry scientific instruments such as cameras and drills to take samples. The rover should also have autonomy and power to cover long distances.
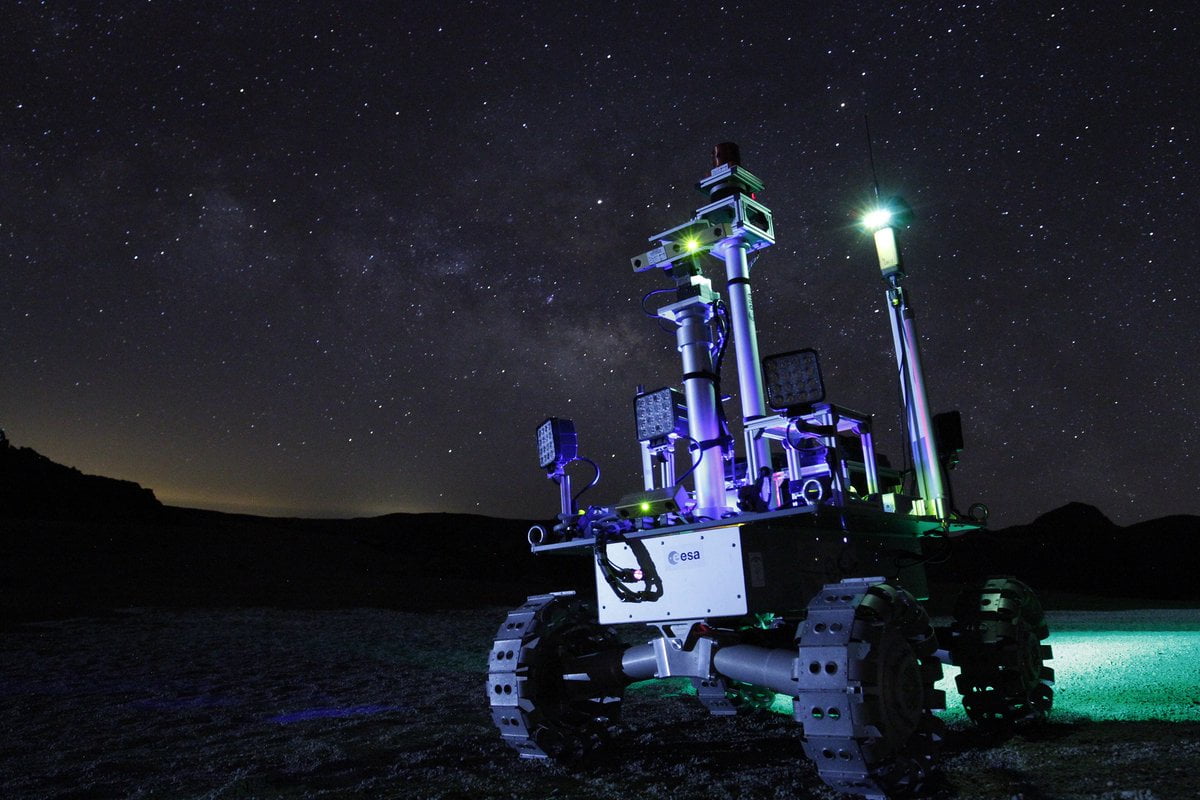

ESA's light-studded Rover Autonomy Testbed
Keywords:
Landing on the moon – Planning and designing a lunar lander
Brief description: In this set of activities, students will plan, design and build a landing module to secure the survival of the crew (in the

Mission on the Moon – Program a classmate to complete a mission on the Moon
Brief description: This activity will introduce students to logical thinking by planning, testing and executing a simple mission on the Moon. Students will work in

Robotic Arm – Become a space engineer for a day
Brief description: In this activity, students will learn how their arm works and build a robotic arm inspired on it. Students will understand the different